1. Array: map, filter, reduce, push, pop, slice
1) map()
- 콜백함수의 리턴을 모아서 새로운 배열을 만들 수 있다.
- 요소를 일괄적으로 변경하는 데 효과적임
배열.map(function(현재값[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]);Callback: 새로운 배열요소를 생성하는 함수로 다음 세가지 인수를 가진다.
- currentValue: 처리할 현재 요소
- index(optional): 처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스
- array(optional): map()을 호출할 배열
- thisArg(optional) : callback을 실행할때 this로 사용될 값
리턴값: 배열의 각 요소의 callback 결과를 모은 새로운 배열
ex)
// 문자열 배열에서 문자열 길이만 획득하기
var arr = ['foo', 'hello', 'diamond', 'A'];
var arr2 = arr.map(function (str) {
return str.length;
});
console.log(arr2); // [3, 5, 7, 1]
2) filter()
- 콜백함수의 리턴을 모아서 새로운 배열을 만들 수 있다.
- 요소를 필터링하기 위한 목적
배열.filter(function(){});
// 정수 배열에서 5의 배수인 정수만 모으기
var arr = [4, 15, 377, 395, 400, 1024, 3000];
var arr2 = arr.filter(function (n) {
return n % 5 == 0;
});
console.log(arr2); // [15, 395, 400, 3000]리턴값은 boolean으로 true인 요소만 모아서 새로운 배열을 만든다.
만족하는 요소가 없다면 undefined가 아닌 빈 배열을 반환한다.
ex) 빈 배열 반환
배열.filter(function(){});
// 정수 배열에서 5로 나누어서 나머지가 1인 정수
var arr = [4, 15, 377, 395, 400, 1024, 3000];
var arr2 = arr.filter(function (n) {
return n % 5 === 1;
});
console.log(arr2); // []
3) reduce()
- 배열을 순회하며 인덱스 데이터를 줄여가며 어떠한 기능을 수행한다.
배열.reduce(function(누적값, 현잿값, 인덱스, 요소){ return 결과 }, 초깃값);reduce 함수는 누적값을 활용한다.
ex)
const products = [
{ id: 'apple', price: 500, description: '사과', amount: 10, },
{ id: 'banana', price: 5000, description: '바나나', amount: 1, },
{ id: 'orange', price: 2500, description: '오렌지', amount: 3, },
{ id: 'avocado', price: 3000, description: '아보카도', amount: 9, },
{ id: 'peach', price: 1500, description: '복숭아', amount: 2, },
{ id: 'kiwi', price: 1000, description: '키위', amount: 4, },
];a: 누적값, b:현재값
const an9Answer = products.reduce(function(a,b){
a += b.price * b.amount;
console.log("price : "+b.price);
console.log("amount : "+b.amount);
console.log("result : "+a);
return a;
}, 0);
console.log(an9Answer);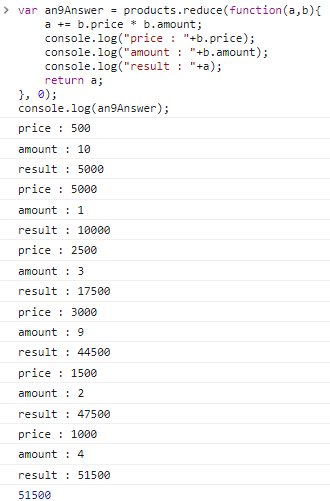
초기값을 꼭 설정해줘야 한다.
ex) 초기값 설정 안할 시
const an9Answer = products.reduce(function(a,b){
a += b.price * b.amount;
console.log("price : "+b.price);
console.log("amount : "+b.amount);
console.log("result : "+a);
return a;
});
console.log(an9Answer);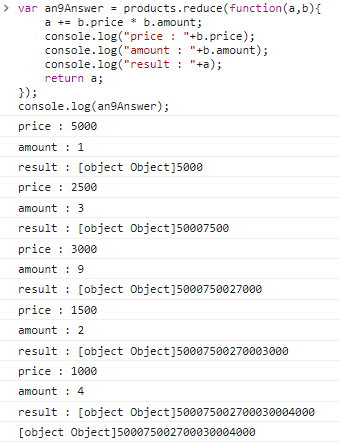
4) push()
기존 배열에 원소 또는 배열을 추가한다.
기존 배열의 값이 변한다.
ex)
const animals = ['pigs', 'goats', 'sheep'];
const count = animals.push('cows');
console.log(count);
// 결과값: 4
console.log(animals);
// 결과값: Array ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows"]
! concat과의 차이점
- push는 기존 배열의 값이 바뀌고 concat은 값을 추가한 새 배열을 만든다.
5) pop()
- 배열에서 마지막 요소를 제거하고 그 요소를 반환한다.
const plants = ['broccoli', 'cauliflower', 'cabbage', 'kale', 'tomato'];
console.log(plants.pop());
// 결과값: "tomato"
console.log(plants);
// 결과값: Array ["broccoli", "cauliflower", "cabbage", "kale"] 하나 빠졌으니까
plants.pop();
console.log(plants);
// 결과값: Array ["broccoli", "cauliflower", "cabbage"] kale이 빠짐.
6) slice()
- 어떤 배열의 begin 부터 end 까지(end 미포함)에 대한 얕은 복사본을 새로운 배열 객체로 반환한다.
const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];
console.log(animals.slice(2));
// 결과값: Array ["camel", "duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(2, 4));
// 결과값: Array ["camel", "duck"]
console.log(animals.slice(1, 5));
// 결과값: Array ["bison", "camel", "duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(-2));
// 결과값: Array ["duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(2, -1));
// 결과값: Array ["camel", "duck"]
console.log(animals.slice());
// 결과값: Array ["ant", "bison", "camel", "duck", "elephant"]
2. Set
- Set 객체는 ES6에서 등장한, 중복을 제거한 값들의 집합이다.
ex) Set 객체 선언
//new Set([iterable]);
let mySet = new Set();
1) 특정 요소 추가: add
- Set 객체에 주어진 값을 갖는 새로운 요소를 추가한다.
//Set.add(value)
mySet.add(1); // Set { 1 }
mySet.add(5); // Set { 1, 5 }
mySet.add('hi'); // Set { 1, 5, 'hi' }
2) 특정 요소 확인: has
- Set 객체에 주어진 값을 갖는 요소가 있는 지 확인(boolean)
// Set { 1, 5, 'hi' }
//Set.has(value)
mySet.has(1); // true
mySet.has(3); // false
mySet.has('hi'); // true3) 특정 요소 제거: delete
- Set 객체에서 주어진 값을 갖는 요소를 제거
// Set { 1, 5, 'hi' }
//Set.delete(value)
mySet.delete('hi'); // Set { 1, 5 }
mySet.delete(1); // Set { 5 }
4) 모든 요소 제거: clear
- Set 객체에서 모든 요소를 제거
// Set { 1, 5, 'hi' }
//Set.clear()
mySet.clear() // Set { }
5) 요소의 개수 반환: size
- Set 객체 내에 있는 요소들의 개수를 반환
// Set { 1, 5, 'hi' }
//Set.size
mySet.size // 3
! 중복 값은 적용 안됨.

3. Object(객체)
- 객체는 관련된 데이터와 함수의 집합니다.
- 여러 데이터와 함수로 이루어지는데, 객체 안에 있을 때는 보통 프로퍼티와 메소드라고 부른다.
ex) 객체 만들기(빈 객체)
var person = {};
person // {}
ex) person 예제
const person = {
name: ['Bob', 'Smith'],
age: 32,
gender: 'male',
interests: ['music', 'skiing'],
bio: function() {
alert(this.name[0] + ' ' + this.name[1] + ' is ' + this.age + ' years old. He likes ' + this.interests[0] + ' and ' + this.interests[1] + '.');
},
greeting: function() {
alert('Hi! I\'m ' + this.name[0] + '.');
}
};
name, age, gender, interests는 문자열이다. 데이터 아이템이며, 이를 '객체의 프로퍼티(속성)'이라 부른다.
bio, greeting 은 함수이다. 이를 '메소드'라 부른다.
1) 점 표기법
person.name
person.name[0]
person.age
person.interests[1]
person.bio()
person.greeting()
2) 괄호 표기법
person.age
person.name.first
person['age']
person['name']['first']한 항목을 선택하기 위해 인덱스 숫자 대신 각 값들과 연결된 이름을 사용하기도 한다.
3) 객체 멤버 설정
- 기존 멤버의 값을 설정하거나, 기존멤버를 새로운 멤버로 대체할 수 있다.
ex) 값 설정
person.age = 45;
person['name']['last'] = 'Cratchit';
person.age // 45
person['name']['last'] // 'Cratchit'ex) 새로운 멤버 생성
person['eyes'] = 'hazel';
person.farewell = function() { alert("Bye everybody!"); }
person['eyes'] // 'hazel'
person.farewell() // Bye everybody!
참조:
https://mesonia.tistory.com/57
JS의 다양한 메소드를 만나보자 (1) map()/reduce()/concat()/push()/filter()/slice()
최근 react를 공부하면서 map, reduce등 배열에 관한 다양한 메소드를 만나고 있다. 무작정 반복문을 써가면서 작업을 하는 것 보다 내장된 메소드들을 잘 알아두고 활용하는게 좋다!! JS의 다양한 메
mesonia.tistory.com
https://miiingo.tistory.com/323,
[Node.js] javascript: Set 객체 사용법
Set 객체 Set 객체는 ES6에서 등장한 중복을 제거한 값들의 집합이다. Set 객체 선언 //new Set([iterable]); let mySet = new Set(); Set 객체 사용 특정 요소 추가: add Set 객체에 주어진 값을 갖는 새로운 요소를
miiingo.tistory.com
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Learn/JavaScript/Objects/Basics
JavaScript 객체 기본 - Web 개발 학습하기 | MDN
이 글에서는 JavaScript 객체와 관련된 기본적인 문법을 살펴보고 이전 코스에서 학습해서 이미 알고 있는 JavaScript 의 특징들과 우리가 이미 사용하고 있는 기능들이 이미 객체와 관련되어 있다는
developer.mozilla.org
'코딩 > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스터디] 3일차(2022.12.17) - 얕은 복사, 깊은 복사 (0) | 2022.12.19 |
|---|---|
| [스터디 2일차] - 일급함수, 고차함수 특징 알아보기 (0) | 2022.12.10 |
| TIL(22.09.28) - Vue js 웹뷰 프로젝트 내 이벤트 함수, 컴퓨터에서는 동작하는데 모바일에서는 동작 안하는 경우 (0) | 2022.09.28 |
| 22.09.17 WIL - Api 연동 시 default값 설정 & 체크박스 설정 (0) | 2022.09.17 |
| 22.08.10 TIL - border-radius 적용 후 여백처리, 자간 조절 (0) | 2022.08.10 |